Market cap shows whether a company is a safe or risky investment. Here are the largest mortgage lenders in the world based on this metric

Updated April 23, 2024
The 10 largest mortgage lenders in the world boast a combined $2.3 trillion in market capitalization. This figure accounts for about a quarter of the $8.9 trillion held by the global banking sector. Also called market cap, the metric is often used by investors to determine if it’s safe or risky to invest in a company.
If you’re an investor considering mortgage lenders to diversify your portfolio, then you’ve come to the right place. If you’re a mortgage broker or just a curious consumer searching for a stable institution to get a home loan, this guide can also prove useful.
In this article, MPA ranks the 10 largest mortgage lenders in the world based on market cap. Read on and take your pick from these banking giants.
Ranking the 10 largest mortgage lenders in the world by market capitalization
Mortgage lenders from the US and China dominate our list. Combined, these banking powerhouses account for almost $2 trillion in market cap. This is equivalent to over four-fifths of the top 10’s total. The UK and India are the other countries represented in our rankings.
These are the world’s 10 biggest mortgage lenders that investors, brokers, and homebuyers must look for.
1. JPMorgan Chase
Market cap: $563.54 billion
Headquarters: New York, USA
Mortgage products: Conventional home loans (fixed- and adjustable-rate mortgages), FHA loans, VA loans, jumbo loans, and mortgage refinancing
JPMorgan Chase & Co. is one of the oldest financial institutions in the US. It is also the country’s largest bank based on market cap. The company offers a range of financial services through Chase Bank, including:
- auto financing
- credit cards
- mortgages
- investment advice
- payment processing
- personal banking
- small business loans
Chase Bank provides mortgages for different types of borrowers in all 50 states. The bank can be a good choice for first-time homebuyers looking for a home loan as it offers no- and low-down-payment options. Some even come with grants and education benefits.
Chase also caters to buyers of expensive homes, offering jumbo loans for properties worth up to $9.5 million. Existing customers who qualify as a Chase Private Client can reduce their interest rates without needing to pay mortgage points.
In 2023, JPMorgan’s loan origination value totaled $35 billion. This was a 46% drop from $65 billion in the previous year. Despite this, JPMorgan & Chase remains the largest mortgage lender in the world based on market cap.

2. Bank of America
Market cap: $291.32 billion
Headquarters: North Carolina, USA
Mortgage products: Home and refinance loans (fixed- and adjustable-rate mortgages), FHA loans, VA loans, jumbo loans, and specialty mortgages
Bank of America (BofA) provides retail banking, wealth management, real estate, and corporate banking services to over 69 million clients worldwide. More than 80% of these are digital customers who use the bank’s wireless payment channels, peer-to-peer money transfers, and its virtual banking assistant called Erica.
In terms of mortgages, BofA offers traditional and refinance loans, including fixed- and variable-rate mortgages. It also issues jumbo mortgages for high-value homes and government-backed FHA and VA loans. The bank’s specialty mortgage product suits doctors whose student debts may be hindering them from qualifying for a traditional home loan. It also offers down payment and closing cost assistance programs.
BofA issued $19.4 billion worth of residential mortgages in 2023. This was a 56% decline from $44.7 billion in the previous year.

3. ICBC
Market cap: $246.51 billion
Headquarters: Beijing, China
Mortgage products: Residential mortgages
The Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC) is the Asian nation’s biggest bank in terms of total assets and market cap. It is also the country’s largest mortgage lender. The financial services giant offers a range of personal and corporate banking solutions to clients in 48 countries.
ICBC’s mortgage products cater to first-time buyers and existing homeowners. In the US, it provides residential home loans in select cities, including New York, Los Angeles, Houston, and Seattle. These mortgages cover single-family homes, condos, and planned unit developments (PUD).
Global clients can also access ICBC’s e-Buy Instant Loan. This product provides a fully digital mortgage journey, from application and approval to lending and tracking.

4. Agricultural Bank of China
Market cap: $202.59 billion
Headquarters: Beijing, China
Mortgage products: Residential home loans, mortgage refinancing
Also known as AgBank, the Agricultural Bank of China is one of the country’s Big Four. It is the third-largest bank in the nation in terms of assets and the second-biggest based on market cap. The firm serves more than 320 million customers and 2.7 million businesses worldwide. It has branches in the UK, Japan, Korea, Singapore, Germany, Australia, and the US.
AgBank offers a range of personal and corporate banking and financial management services. It specializes in products catering to agro-related businesses. These include credit facilities, payment processing, cash management, and trading.
AgBank provides mortgages for new and existing homes. Clients can choose between fixed and variable rates in varying term lengths. The bank also offers mortgage loan refinancing and wealth management-linked housing loan accounts.
5. Wells Fargo
Market cap: $200.66 billion
Headquarters: California, USA
Mortgage products: Fixed- and adjustable-rate mortgages, jumbo loans, government-sponsored loans, cash-out refinance
Wells Fargo is one of the world’s largest financial service holding firms. It offers a range of retail and wholesale banking and wealth management services for individuals and businesses. These include commercial and consumer loans, card products, deposit and transaction services, and agricultural financing. The firm serves more than 70 million clients globally.
In 2023, Wells Fargo announced that it would cease offering mortgage products to new clients. The company, however, continues to serve existing borrowers. Because of the move, the company’s loan originations shrunk to $1.1 billion last year from $44 billion in 2022. Still, the firm ranked as the second-largest mortgage lender in the US.
6. Bank of China
Market cap: $165.15 billion
Headquarters: Beijing, China
Mortgage products: Residential home loans, reverse mortgages, mortgage partnership finance (MPF)
Bank of China is the country’s oldest existing bank. It offers wealth management and private and corporate banking services to clients in more than 60 countries and regions. The bank’s portfolio includes deposits, investments, insurance, and credit cards.
Bank of China provides mortgages for first-time homebuyers, government housing, and green residential projects. It also has a reverse mortgage program with fixed rates and varying term lengths. In certain regions, borrowers can receive rewards by using the mobile app in their transactions.

7. China Construction Bank
Market cap: $156.46 billion
Headquarters: Beijing, China
Mortgage products: Traditional home loans, account-linked mortgages, reverse mortgages
The last of China’s Big Four on the list, China Construction Bank (CCB) is also among the world’s largest mortgage lenders. CCB offers a range of personal and corporate banking services. These include e-banking, deposits, credit cards, and fund settlements. The bank serves around 3.5 million businesses and 314 million individual clients in 29 countries.
CCB provides fixed- and variable-rate mortgages for different types of homes. It lets borrowers link their savings accounts to their homes. The bank also has a reverse mortgage program with flexible terms.
8. HSBC
Market cap: $152.25 billion
Headquarters: London, UK
Mortgage products: Conforming home loans, jumbo mortgages
HSBC Holdings plc serves around 42 million customers in more than 60 countries and territories. This makes it one of the world’s largest financial institutions. HSBC provides wealth management, loan, and banking services. These include cross-border banking.
In terms of home loans, borrowers can access fixed- and adjustable-rate mortgages and jumbo loans. The bank also offers a range of mortgage features exclusive to account holders. These features vary depending on the clients’ personal deposit and investment balances.
.png)
9. Morgan Stanley
Market cap: $150.90 billion
Headquarters: New York, USA
Mortgage products: Residential mortgages
Morgan Stanley is a global investment bank and financial services firm. It offers solutions tailored to a wide range of businesses, from startups to multinational conglomerates. The company operates in more than 40 countries.
Morgan Stanley’s portfolio includes:
- banking
- brokerage and investment advisory services
- financial and wealth management services
- annuity and insurance products
- credit and other lending products
- retirement plan services
The financial services giant offers mortgages through the Morgan Stanley Private Bank, National Association (MSPBNA). Its products include fixed- and adjustable-rate home loans. US clients can reduce or eliminate the need for a down payment through the loan’s asset pledge feature. This uses qualified securities from their Morgan Stanley brokerage account as collateral.

10. HDFC Bank
Market cap: $150.11 billion
Headquarters: Mumbai, India
Mortgage products: Traditional home loans, home renovation and extension loans, bridge mortgages, plot loans, rural housing loans, mortgage refinancing
HDFC Bank is India’s biggest private sector bank and the country’s largest mortgage lender. It provides retail and corporate banking, home loan, and treasury services to more than 120 million clients. Apart from India, the company operates in the UK, Singapore, the Middle East, Africa, and the Asia-Pacific region.
HDFC offers mortgages for various types of housing. These include rural housing for farmers and other members of the agricultural sector. It also issues loans for home renovations and extensions and purchasing plots of lands. Borrowers can access short-term bridge loans for funding new home purchases until the sale of their existing property.
Here’s a recap of the top 10 largest mortgage lenders in the world.
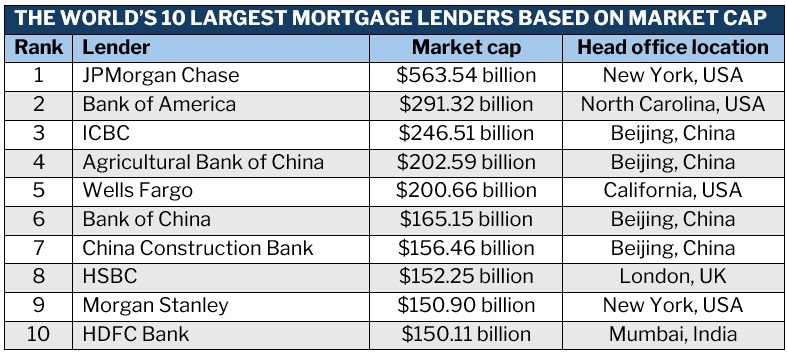
Top 10 largest mortgage lenders in the world by market cap
What is market capitalization and why is it important?
Market capitalization, also called market cap, is the total market value of a company’s outstanding shares owned by stockholders. In layman’s terms, it shows how much a company is worth as determined by the stock market.
Market cap is often used by investors to get a clear picture of a company’s size without having to look for its overall assets or revenue numbers. It is a vital metric for the investing community. The market cap can reveal if an organization is a safe investment or if it presents too high of a risk.
In general, companies with a large cap are considered financially stable and carry less risk for investors. Businesses with smaller market caps, meanwhile, are seen as riskier investments. These companies, however, provide opportunities for huge returns, especially if they post significant growth.
To calculate market capitalization, you need to multiply the number of a company’s outstanding shares by the current market value of a single share. For the rankings, MPA pulled market cap figures from this website. We restricted the list to banks; no non-bank lenders were included. The figures are up to date as of April 2024.
If you’re looking for a good mortgage lender to either invest in or provide a home loan to your clients, MPA’s Best in Mortgage Special Reports page is the place to go. Here, we feature individuals and companies that are recognized as respectable and trusted market leaders. By partnering with these industry leaders, you can be sure that you’re doing business with those who have your clients' best interests in mind.
Have you experienced working with the world’s largest mortgage lenders? How was it? We’d love to see your story below.



